Difference between revisions of "IMedA"
(Created page with "{{ResearchProjInfo |Title=iMedA |ContactInformation=Slawomir Nowaczyk |ShortDescription=Improving MEDication Adherence through Person Centered Care and Adaptive Interventions ...") |
|||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ResearchProjInfo | {{ResearchProjInfo | ||
| − | |Title= | + | |Title=IMedA |
|ContactInformation=Slawomir Nowaczyk | |ContactInformation=Slawomir Nowaczyk | ||
|ShortDescription=Improving MEDication Adherence through Person Centered Care and Adaptive Interventions | |ShortDescription=Improving MEDication Adherence through Person Centered Care and Adaptive Interventions | ||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
The iMedA agent will be built by combining three important AI techniques. First is to create a meaningful and comprehensive representation of each patient based on information fusion and representation learning. Second is to use peer group analysis and interpretable supervised machine learning methods to predict non-adherence for concrete patients. Finally, intervention strategies that are the most appropriate for a particular patient we will selected by combining data-driven and knowledge-driven approaches. | The iMedA agent will be built by combining three important AI techniques. First is to create a meaningful and comprehensive representation of each patient based on information fusion and representation learning. Second is to use peer group analysis and interpretable supervised machine learning methods to predict non-adherence for concrete patients. Finally, intervention strategies that are the most appropriate for a particular patient we will selected by combining data-driven and knowledge-driven approaches. | ||
| − | + | |LogotypeFile=iMedA.png | |
| − | |LogotypeFile= | ||
|ProjectResponsible=Slawomir Nowaczyk | |ProjectResponsible=Slawomir Nowaczyk | ||
| + | |ProjectDetailsPDF=Final iMedA.pdf | ||
| + | |FundingMSEK=3 | ||
|ProjectStart=2017/11/20 | |ProjectStart=2017/11/20 | ||
|ProjectEnd=2020/11/19 | |ProjectEnd=2020/11/19 | ||
| − | |ApplicationArea= | + | |ApplicationArea=Health Technology |
}} | }} | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
{{ShowResearchProject}} | {{ShowResearchProject}} | ||
| − | [[Image:iMedA.png| | + | [[Image:iMedA.png|750px]] |
| + | |||
| + | Funded by Vinnova: | ||
| + | https://www.vinnova.se/e/digital-halsa/artificiell-intelligens-for-battre-halsa/ | ||
Latest revision as of 20:26, 21 May 2019
Improving MEDication Adherence through Person Centered Care and Adaptive Interventions
| IMedA | |
| Project start: | |
|---|---|
| 20 November 2017 | |
| Project end: | |
| 19 November 2020 | |
| More info (PDF): | |
| [[media:Final iMedA.pdf | pdf]] | |
| Contact: | |
| [[Slawomir Nowaczyk]] | |
| Application Area: | |
| [[Health Technology]] | |
Involved internal personnel
| |
Involved external personnel
| |
Involved partners
| |
-
| |
Abstract
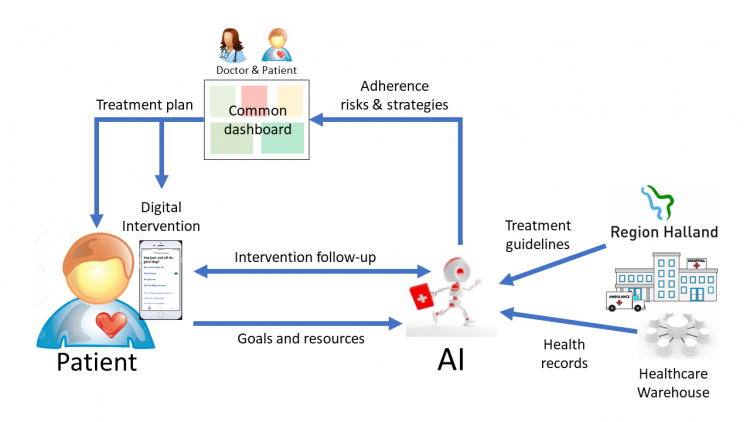
The iMedA project will improve medication adherence for hypertensive patients through an AI agent that supports doctor and patient in collaboratively understanding key individual adherence risk factors and designing an appropriate intervention plan. iMedA will deliver the selected intervention through a mobile App and follow-up on its effectiveness improving the system over time. The combination of person-centered care and self-management interventions will lead to significantly improved health outcomes and reduced healthcare costs.
iMedA empowers hypertensive patients to take responsibility for their health through self-management, and provides doctors with information they need for person-centered care. To identify risks and intervention strategies, iMedA uses health records as well as self-reported input. The AI agent understands how both medical and personal factors interact with respect to medication adherence, and display this information on a "dashboard" that guides patient-doctor conversation. The AI monitors the effectiveness of interventions in order to improve over time.
The iMedA agent will be built by combining three important AI techniques. First is to create a meaningful and comprehensive representation of each patient based on information fusion and representation learning. Second is to use peer group analysis and interpretable supervised machine learning methods to predict non-adherence for concrete patients. Finally, intervention strategies that are the most appropriate for a particular patient we will selected by combining data-driven and knowledge-driven approaches.
Funded by Vinnova: https://www.vinnova.se/e/digital-halsa/artificiell-intelligens-for-battre-halsa/